The Great Wall: One of Seven Wonders on Earth
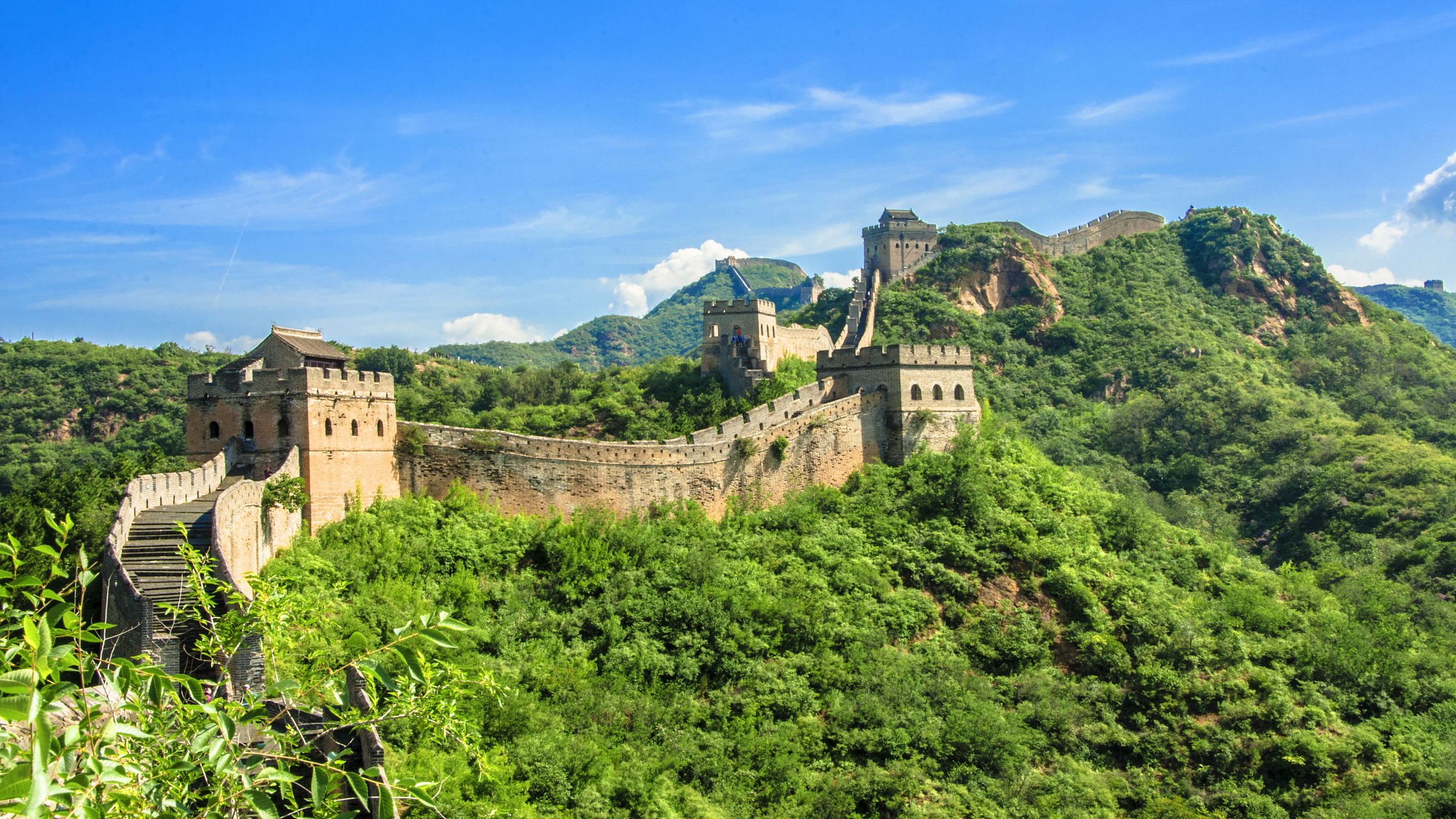

A picture of Jinshanling Great Wall in Hebei province. (PHOTO: VCG)
By?BI?Weizi
The Great Wall of China is one of the longest and most extensive ancient defense projects in the world. Construction of the wall continued for more than 2,000 years, beginning in the Western Zhou Dynasty (1045– 771 BC). Its vast coverage spans? northern and central China, with a total length of more than 20,000 kilometers.
The general principle of "constructing military defense systems by taking advantage of natural geographic hazards" has been applied since the first emperor of Qin, who destroyed six states and unified the country, further used the Great Wall in the third century B.C. as an important means to prevent the invasion of northern nomads. The structures of the wall are varied according to the terrain. This architectural design makes the Great Wall easy to defend and difficult to attack, greatly enhancing its defensive and offensive functions.
The basic materials used to build the wall during the Qin Dynasty included earth, stone, wood, and brick. The materials were always sourced locally, so different parts of the wall reflect what was available in the surrounding area.
In the high mountains, stone was quarried from the land. In flat areas, soil was used to create a compacted layer of earth. In the Gobi Desert area, sand, pebbles, tamarisk branches, and reeds were used in alternating piles. In the northeast, oak and pine planks were used. With the progress of social productivity and brick-making technology, many parts of the Ming Great Wall were built with huge brick masonry.
The construction and garrisoning of the Great Wall have been instrumental in the formation and development of a pluralistic pattern of the Chinese people.
On March 4, 1961, the Great Wall was announced by the State Council as the first batch of national key cultural relics protection units. In December 1987, the Great Wall was listed as a World Heritage Site.